All published articles of this journal are available on ScienceDirect.
The Effectiveness of Learning Implementation Plan Tool Through Design-Based Research
Abstract
Background:
Research of Program for International Student Assessment (PISA) focusing on reading material, mathematics, and Natural Science shows that Indonesia ranks 10th of the lowest from 65 countries. Research of Trends International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) shows the Indonesian students capability at very low rank in 1) understanding complex information, 2) theory, analysis, and problem solving, 3) use of tools, procedures, and problem solving, and 4) investigation. One possible way to overcome the problem of Indonesian students’ weakness is to improve the Lesson Plan.
Materials and Methods:
This research intended to determine the effectiveness of Science-Biology Lesson Plan through design-based research. The research used Tessmer Model with the stages of self-evaluation, expert reviews, one by one, small group, and field test as the research focus. The research subject was VII A students amounted to 40 students. The data included 1) cognitive learning outcomes, 2) performance skills, 3) character behavior, 4) social skills, and 5) critical thinking skills. Learning outcomes was obtained through test and analyzed based on Minimum Mastery Criteria. Performance skills were assessed through observation using performance task detail rubric. Character behavior and social skill were assessed through observation using characteristic behavior rubric. Critical thinking skills were ssessed through student worksheets with quantitative rubric.
Results:
The research result shows that Lesson Plan is effective to be used based on (1) student learning outcomes (product and process) that have exceeded the classical completeness, (2) student performance skills are very good, (3) student character behavior (discipline and responsibility) is very good, (4) student social skills (collaborating and contributing ideas) are mostly very good, and (5) student critical thinking skills are good.
1. INTRODUCTION
The main key to deal with all 21st century challenges is scientific literacy [1]. Scientific literacy can be meant as knowledge and scientific skill to identify questions, gain new knowledge, explain scientific events, draw conclusion based on the facts, understand the nature of science, awareness of science and technology linkage, as well as have a concern for science issues [2]. Therefore, scientific literacy deals with several scientific skills.
The results of National Research Council (NRC) workshop 2007 on 21st century skills define five skills that needs to be improved namely adaptation, complex communication skills, non-routine problem-solving skills, self-management/self-development, and thinking systems. The next workshop results focus on three skills in learning, namely [1] cognitive skills (non-routine problem solving, critical thinking, thinking systematically), [2] interpersonal skills (complex communication, social skills, teamwork, cultural sensitivity, diversity), [3] interpersonal skills (self-management, time management, self-improvement, self-regulation, adaptability, and executive function).
The research results of Trends International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) on 2015 positioned Indonesia at 44th rank of 47 countries in the field of science [3]. This indicates that the scientific literacy of students is still low. Several factors have significant impact on scientific literacy development of students in learning, namely learning model, facilities, learning resources, teaching materials, and etc. [4]. The important thing is to design the learning and conduct assessments that can stimulate the scientific literacy increase. One way that may facilitate improving scientific literacy is to design contextual learning based on the students’ environmental condition.
The lesson design is compiled into a tool called Lesson Plan Tool (RPP Tool). According to the Regulation of Minister of National Education number 41 of 2007, Lesson Plan tool consists of syllabus, Lesson Plan, Student Worksheet and the answer key, teaching materials, learning media, and evaluation tools. Lesson Plan tool can affect learning outcomes. In addition, several matters related to learning process such as learning strategy, student, and teacher also affect learning outcomes [5].
Learning design is made by referring to 2013 Curriculum. The 2013 Curriculum is designed to improve the competence of knowledge, skill, and attitude comprehensively. Teachers are required to be more creative in teaching, improving teaching skill, and developing pedagogically in the learning process [6]. This is reasonable because Indonesian student’s ability is at low rank in understanding 1) complex information, 2) theory, analysis, and problem solving, 3) use of tools, procedures, and problem solving, as well as 4) investigation [7].
The challenges for teachers are teaching concepts, processes, and thinking skills comprehensively to students. Therefore, a learning should be planned, assessed, and evaluated. A teacher is required to plan varied learning strategies with the principles of learning and empowering students, not just teaching students [8]. Students learn by experiencing themselves, constructing knowledge, then providing explanation to the knowledge [8].
Planning, assessing, and evaluating Lesson Plan tool is a means to improve the product [9]. It can be performed through design-based research [10]. The main purpose is to obtain high quality product and one of them is product effectiveness, namely the prototype of Lesson Plan tool.
Design-based research is relevant to educational practices and policies because the intention is to solve the complex issues on research-based on educational practices or to improve and validate the learning theory [11]. According to Ritland [12], since the early 1990s in educational research, the term “design” is used as an experimental design in educational research. Design-based research is not enough with just a single approach but requires a series of approach [13].
Lesson Plan tool in school needs to be evaluated and revised through development research. This research process is an iterative design focusing on the implementation and development of intervention/product in education [14]. The term ‘development research’ is popularized by Richey & Klein [15] as design and development research namely a systematic research of design, development, and evaluation that intends to generate learning/non-learning product. There are two paradigms in design-based research, namely design to solve problems, and design as reflection in action [16].
Lesson Planning tool development research is an innovation for learning process. By this way, a valid, practical, and effective product will be generated [11]. Product of development results is valid (relevant) due to intervention and design based on state-of-the-art knowledge [11]. Tessmer [17] described the practical term where the users are free to use the product in the learning environment and it is said to be effective if a goal can be achieved according to specific questions and criteria.
Lesson Plan tool development is according to the Regulation of Ministry of National Education Number 65 of 2013 on ICT utilization. This requires the learning to prepare students for global era. The demands of 21st century students’ skills are how to think critically, find solutions, be creative, and gain information and media skills required in learning using CST.
Rotherdam & Willingham [18] described that success of students depends on their ability to think critically, solve problems, communicate and collaborate. Inquiry-based learning provides opportunity to teachers to explore critical thinking and creative thinking skill. Both of the thinking skills are high order thinking skills which are always emphasized in modern science learning. Lohner et al. [19] stated that inquiry learning offers authentic experience by involving students in the process of knowledge construction. Inquiry-based learning in science involves the process of science and thinking skills. This model is also called 'guided discovery'. Teacher guides students’ inquiry until they ‘discover’ the concept of science that has been determined by the teacher [20].
The implementation of inquiry-based learning has succeeded in increasing students’ activity, improving learning and learning outcomes, as well as scientific attitudes [21-23]. Inquiry-based learning is also able to improve character of student and learning activity [24, 25]. This success needs to be continued to determine the effectiveness of different topics and levels through design-based research.
2. RESEARCH METHOD
A good method can lead the researcher in achieving the research objective [26-28], in which this research was a product development research in the form of learning implementation plan tools (syllabus, lesson plan, worksheet, and teaching materials) based on guided inquiry model. The research procedures referred to Tessmer model namely self-evaluation, expert reviews, one by one, small group, and field test as the research focus [9]. One of the qualities that a developed product should possess is effectiveness which is determined based on the field test data.
This research was conducted for a month in one of the junior high schools. The research was conducted in a classroom. Field test stage involved 40 students of VII Grade and a subject teacher of Natural Science as the research partner.
The type of data to determine the effectiveness of learning implementation plan tool includes 1) cognitive learning outcomes, 2) performance skills, 3) character behavior, 4) social skills, and 5) critical thinking skills. Each assessment is referred to the assessment sheet instrument.
- Cognitive assessment sheets: (a) cognitive assessment sheet of product was used to measure students’ mastery over the learning materials. This instrument consisted of pretest and post-test in form of 20 multiple-choice questions that performed for less than in 15 minutes; (b) cognitive process assessment sheet was used to measure students’ mastery over the learning activities performed which consisted of pretest and post-test in form of 5 multiple-choice questions that was performed in less than 5 minutes and the validated questions from expert review were majorly used for cognitive assessment [29].
- Performance skill assessment sheet. This instrument was provided to assess students’ skills in using tools during teaching and learning activities. The instrument was in a form of observation sheet with assessment rubric. This assessment involved the observer who assessed student psychomotor during the learning process. Instrument format was adapted from Nur [29].
- Student’s behavior and character assessment sheet. This instrument was used to assess student’s behavior and character during learning process. The instrument was in a form of observation sheet with assessment rubric. The observer provided score based on the available rubric for assessment format. Instrument format was adapted from Nur [29].
- Student’s social skills assessment sheet. This instrument was used to assess student’s social skills during the learning process. The instrument was in the form of observation sheet with assessment rubric. The observer provided a score based on the available rubric for assessment format. Instrument format was adapted from Nur [29].
- Student’s critical thinking skill assessment sheet. This instrument was used to assess students’ critical thinking skill through their answer on the worksheet. The observer provided a score based on the available rubric for assessment format. The instrument format was adapted from Herlina [30].
Analysis of effectiveness data obtained from the assessment data during field test was conducted descriptively. Data analysis techniques of each learning outcomes are explained in more detail as follows:
- Cognitive assessment result. The result observed from the cognitive assessment is classical completeness. Learning was considered as effective if it exceeded the classical completeness of 85%. Classical completeness was obtained from the number of students who individually fulfilled the criteria. Students were considered to have fulfilled the criteria individually if the value was obtained at least in accordance with minimum mastery criteria of 70. The formula to obtain cognitive result is:
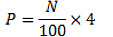 |
Description:
P = Pretest/Post-test value
N = student score
Based on the individual completeness, then the classical completeness could be determined by formula:
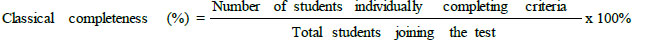 |
Classical completeness result was analyzed descriptively.
1. The result of performance skill and critical thinking skill assessment of each student was obtained by formula:
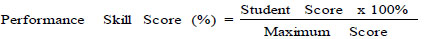 |
The result of all students was average and converted into percent for each meeting. The result was described in descriptively.
2. The result of behavior character and social skills assessment of each student was obtained by formula:
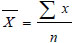 |
Description:
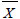 = average of activities
= average of activities
∑X = sum of activities
n = the number of activities
The result of entire students was averaged and converted into percent for each meeting. The result was described descriptively.
3. RESULT
Table 1 shows cognitive learning result of the product as well as the process that passes beyond the classical completeness at post-test. The results of student performance skills are presented in Table 2 .
| Test | Students Who Took the Test (People) | Students Completing Criteria (Person) | Students not Completing Criteria (Person) | Classical Completeness (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product | Pretest | 40 | 1 | 39 | 2.56 |
| – | Post-test | 37 | 3 | 92.5 | |
| Process | Pretest | 0 | 40 | 0 | |
| – | Post-test | 37 | 3 | 92.5 | |
| Average of Student Performance Skill Results Achievement at Meeting of- | Average of Entire Meetings | Category | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 97.3 | 99.2 | 96.1 | 96.9 | 96.1 | 97.12 | Very Good |
Table 2 shows very good student performance skills. The results of student behavior character are presented in Table 3.
| Observed Attitude | Average Behavior Character Achievement at Meeting of- | Average of Entire Meetings | Category | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| Discipline | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Very Good |
| Responsibility | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Very Good |
Table 3 shows very good student behavior character (discipline and responsibility). The results of student social skills are presented in Table 4.
| Observed Attitude | Average Social Skills Achievement at Meeting of- | Average of Entire Meetings | Category | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| Collaborating | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Very Good |
| Contributing Ideas | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Very Good |
Table 4 shows very good student social skills (collaborating and contributing ideas). The results of student critical thinking are presented in Table 5 that shows very good student critical thinking skills.
| Average Critical Thinking Skill Results Achievement at Meeting of- | Average of Entire Meetings | Category | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 76.40 | 87.80 | 80.00 | 89.12 | 87.70 | 76.40 | Good |
The research result shows that Lesson Plan is effective to be used based on student learning outcomes (product and process) that have exceeded the classical completeness, students’ performance skills that are above the average, student character behavior (discipline and responsibility) that is above the average, student social skills (collaborating and contributing ideas) that are above the average, and students critical thinking skills that have reached the average.
4. DISCUSSION
The effectiveness indicators of lesson plan tool are cognitive learning outcomes, performance skill, character behaviors, social skills, and critical thinking skills. Learning outcomes of students (product and process) have exceeded the classical completeness. This is in line with previous research [22, 24, 25, 31] that they conducted inquiry-based learning and assisted students in finding their own answers to solve a problem. This learning emphasizes the process, although it does not neglect the product.
Student performance skill is very good because almost all groups can use the equipment based on the details of performance tasks that have been prepared by teacher. Sanjaya [32] stated that direct learning is student’s experience as the results of their activities. Students experienced and felt by themselves everything related to the goal achievement.
Performance skills are very good. These findings are in line with previous research [33, 34] that inquiry-based learning cannot be separated from students’ activities in implementing experiment. Furthermore, the use of student worksheet oriented to approach of environmental-based science process skills has positive effect to students learning outcomes improvement on the performance aspects [33].
The very good student performance skills generate a good student process skill [35, 36]. Blessinger [37] and Sanjaya [38] explained that inquiry-based learning emphasizes on the aspects of cognitive, affective, and psychomotor in balance. Consequently, the learning is considered to be more meaningful.
Character behaviors use the indicator of discipline and responsibility well. This is in line with the previous research [39]. She explained the inquiry-based Lesson Plan tool successfully instilled the character values. Student’s character shows positive result through guided inquiry [40]. Other research reported that the very good characters appeared are independent, curious, tolerance, creative, discipline, collaboration, and responsibility [41].
Inquiry based learning according to Shoimin [42] emphasizes on the development of cognitive aspect, affective, and psychomotor in balance, so the learning is considered to be more meaningful. Moreover, this kind of learning is in accordance with psychological development of modern learning which considers learning a process of behavioral change.
Most of students’ social skills (collaborating and contributing ideas) are very good. Social knowledge cannot be formed from a person action on an object, but it is formed through the interactions with others Wadsworth in Sanjaya [32]. This is the essence of social skills. When student interacts with their friends, then the opportunities to build social knowledge can develop.
The observation result of social skill using indicators of collaboration and contributing ideas is good. This is in line with previous research that the developed Lesson Plan tool shows student competence improvement because inquiry syntax can accommodate competences of spiritual, social, knowledge, and skills [43]. Inquiry-based learning is designed with aims to make students have scientific skills and directly involved in the learning process [44].
Good critical thinking skill is supported by previous research [21, 44-46]. Critical thinking skill in students’ groups of inquiry-based learning is better than the control group [44]. Inquiry-based learning is positively correlated to the student critical thinking ability [21]. Inquiry-based learning has significant positive impact on student critical thinking skills [46]. The student critical thinking skills (formulating problems, formulating hypotheses, collecting data, analyzing data, and drawing conclusion) are also in good category generally [45].
Critical thinking skill is required and must be owned by students [47]. The developed student worksheet is effective to improve student critical thinking skill. Critical thinking skill is one of the learning instrument effectiveness indicators [48].
CONCLUSION
Based on the research results, the effective Lesson Plan tool is based on student outcomes (product and process) that have exceeded classical completeness, student performance skill is very good, student character behavior (discipline and responsibility) is very good, most of student social skills (collaborating and contributing ideas) are very good, and student critical thinking skills are good.
ETHICS APPROVAL AND CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE
Not applicable.
HUMAN AND ANIMAL RIGHTS
No Animals/Humans were used for studies that are the basis of this research.
CONSENT FOR PUBLICATION
Not applicable.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The author declares no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
On this occasion I would like to express my gratitude and express my highest appreciation to the Dean of the Faculty of Teacher Training and Education at Universitas Lambung Mangkurat who has provided assistance with the cost of writing this article. Not forgetting, I also convey an immeasurable appreciation to Dr. J Dalle who have helped improve this article so that it is worthy of being accepted and published in international journals.


